
In forex trading, having the right strategy can mean the difference between success and failure. With numerous options available, understanding the various forex trading strategies and their pros and cons is crucial for traders of all levels. In this trading lesson, we’ll discuss the top 12 forex trading strategies, providing insights, examples, and practical advice to help you successfully trade the forex market.
What is a Forex Trading Strategy?
A forex trading strategy serves as a roadmap for traders, guiding them on when to enter, manage, and exit trades. Whether based on technical analysis or fundamental factors, a well-defined strategy is essential for achieving consistency and managing risk in the forex market.
Factors to Consider When Choosing The Best Forex Trading Strategy
Selecting the right forex trading strategy requires careful consideration of several factors, including:
Time frame
Different strategies are suited to various time frames, from short-term day trading to long-term position trading. Choose a strategy aligned with your trading style and time availability.
Number of trading opportunities
Consider how frequently you want to trade. Scalping strategies offer numerous opportunities within a day, while position trading involves fewer trades but over longer periods.
Position size
Determine the appropriate position size based on your risk tolerance and account size. Some strategies, like scalping, may require smaller position sizes due to higher frequency trading.
12 Best Forex Trading Strategies: A Top-level Overview
Let’s analyze the top 12 forex trading strategies, each with its unique characteristics, pros, and cons:
-
Price Action Trading
Price action trading is a strategy that focuses on analyzing and making trading decisions based solely on the movement of prices on a chart, without relying on traditional technical indicators.
Consider the following example of a price action trade on the EUR/USD currency pair:
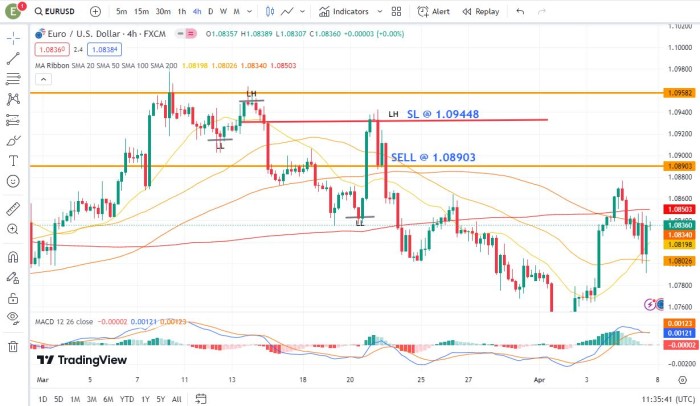
In this illustration, the trader identifies a clear downtrend in the EUR/USD pair based on lower lows and lower highs. Using price action analysis, the trader identifies a key resistance level near 1.09582, where price has previously stalled multiple times.
The trader waits for a bearish price rejection candlestick pattern, such as a bearish engulfing pattern or a shooting star, to form near the resistance level. Once the pattern appears, the trader enters a short position at 1.08903 with a stop-loss placed above the recent swing high at 1.09448. As expected, price reverses lower after the bearish rejection pattern, allowing the trader to capture a profit from the downward movement.
Pros
- Clean Charts: Price action trading simplifies charts by removing clutter caused by numerous technical indicators. Traders can focus solely on price movements, leading to clearer analysis and decision-making.
- Reduced Risk of Information Overload: By eliminating the need for multiple indicators, price action traders can avoid information overload and conflicting signals.
- Enhanced Market Understanding: Price action trading requires traders to develop a deep understanding of market dynamics, including support and resistance levels, trendlines, and chart patterns.
Cons
- Keen Understanding Required: Price action trading demands a thorough understanding of market dynamics and chart patterns.
- Subjectivity: Unlike traditional technical indicators, which provide objective signals, price action analysis can be subjective.
-
Range Trading Strategy
Range trading is a forex trading strategy that entails identifying specific price levels, known as support and resistance, where a currency pair tends to consolidate or trade within a defined range over a certain period. Traders employing this strategy aim to profit from the repetitive nature of price movements within this range-bound environment by buying near support levels and selling near resistance levels.
This approach relies on the principle that price tends to oscillate between established support and resistance zones. Thus, providing opportunities for traders to enter and exit trades based on these key price levels.
Consider the following illustration of a range trading setup on the USD/JPY currency pair:
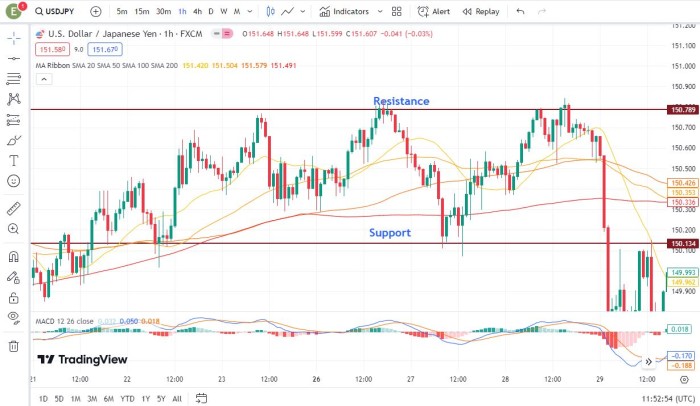
In this example, the USD/JPY pair has been trading within a defined range between 150.134 (support) and 150.789 (resistance) for an extended period. Traders can identify potential buy opportunities near the support level and sell opportunities near the resistance level.
Traders can enter long positions when price approaches the support level, with stop-loss orders placed below the support level to manage risk. Conversely, short positions can be initiated when price nears the resistance level, with stop-loss orders placed above the resistance level.
As price oscillates within the established range, traders can profit from the repetitive nature of price movements by executing trades at strategic support and resistance levels.
Pros
- Clear Trading Ranges: Range trading provides clear boundaries within which price tends to fluctuate, making it easier to identify potential trade setups.
- Predictable Price Movements: By trading within established ranges, traders can anticipate price reversals at support and resistance levels.
- Suitable for Choppy Markets: Range trading performs well in markets lacking a clear trend, such as sideways or ranging markets.
- Defined Risk and Reward: Traders can set precise entry and exit points based on support and resistance levels, allowing for effective risk management.
Cons
- Limited Profit Potential: Range trading restricts profit potential as traders aim to capitalize on short-term price fluctuations within the established range.
- False Breakouts: Breakouts from range-bound conditions can lead to false signals, resulting in losses for traders who enter prematurely.
- Requires Patience: Traders must exercise patience and discipline to wait for price to reach support or resistance levels before entering trades.
- Risk of Range Expansion: Sudden market shifts can lead to range expansion, invalidating established trading ranges and causing losses for range traders.
-
Trend Trading Strategy
Trend trading involves identifying and following the prevailing direction of a currency pair’s price movement over time. Traders employing this strategy seek to capitalize on sustained price movements in the direction of the prevailing trend.
Traders use technical analysis tools to identify trends, such as moving averages or trendlines. Once a trend is identified, traders enter positions in the direction of the trend, aiming to ride the momentum for potential profits.
Trend traders implement risk management techniques, such as setting stop-loss orders, to protect against adverse price movements. Position sizes are determined based on factors such as risk tolerance and the strength of the trend.
Consider the following illustration of a trend trading setup on the GBP/USD currency pair:
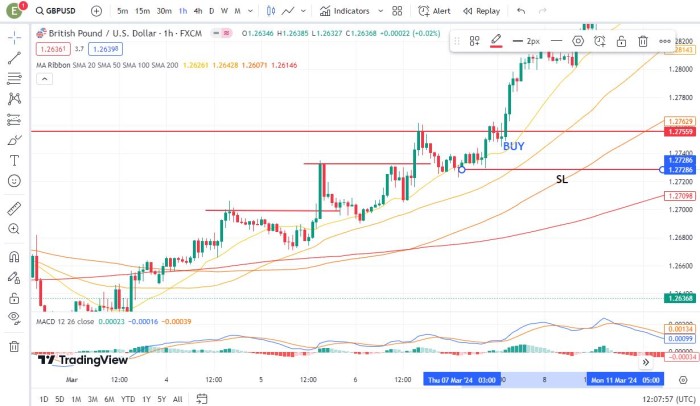
In this example, the GBP/USD pair exhibits a clear uptrend, characterized by higher highs and higher lows. Trend traders would enter long positions to capitalize on the upward momentum of the trend.
A trader will enter a long position as the price breaks above a key resistance level at 1.27629, expecting the uptrend to continue. He then manages his risk by placing a stop-loss order below the recent swing low at 1.27286. By effectively implementing a trend trading strategy, the trader aims to profit from the sustained upward movement of the GBP/USD pair.
Pros
- Profit Potential: Trend trading offers significant profit potential during strong and sustained trends.
- Clear Direction: Traders benefit from clear directional signals provided by established trends.
- Reduced Market Noise: Trend traders filter out market noise and focus on trading opportunities aligned with the prevailing trend.
Cons
- Trend Reversals: Sudden trend reversals can result in losses for trend traders who fail to adapt quickly.
- Late Entries: Delayed entry into a trend can diminish profit potential or increase risk.
- False Signals: Trend traders may encounter false signals during periods of market consolidation or choppy price action.
-
Position Trading
Position trading is a strategy where traders hold positions for weeks, months, or even years to capitalize on long-term market trends. Traders employing this strategy focus on fundamental analysis and macroeconomic factors to identify opportunities with significant profit potential. This strategy relies heavily on fundamental analysis to assess economic indicators, geopolitical events, and market sentiment.
Position traders require patience and discipline to withstand short-term fluctuations and adhere to their trading plan. Effective risk management is essential to protect capital over the extended duration of trades.
Pros
- Profit Potential: Position trading offers the potential for substantial profits from major market trends.
- Reduced Stress: Traders can avoid the stress of frequent trading decisions associated with shorter-term strategies.
- Flexibility: Position traders have the flexibility to participate in other activities while their trades unfold.
Cons
- Drawdowns: Extended holding periods may lead to larger drawdowns during adverse market conditions.
- Opportunity Cost: Missed opportunities to profit from shorter-term price movements may occur while holding positions.
- Requires Patience: Position trading requires patience to wait for trades to unfold and reach their profit targets.
5. Day Trading Strategy
Day trading is a strategy where traders open and close positions within the same trading day to capitalize on short-term or intraday market movements. Traders employing this strategy focus on technical analysis and short-term price fluctuations to identify intraday trading opportunities. This strategy relies on technical indicators, chart patterns, and intraday market dynamics to make trading decisions.
Day traders must make rapid decisions to enter and exit trades efficiently during the trading session. Effective risk management is essential to limit losses and preserve capital amidst intraday market fluctuations.
Pros
- High Potential Returns: Day trading offers the potential for significant profits from short-term price movements.
- Liquidity: Day traders focus on liquid markets with high trading volumes, providing ample opportunities for trade execution.
- No Overnight Exposure: Day traders do not hold positions overnight, reducing the risk associated with overnight market events.
Cons
- High Stress Levels: Rapid decision-making and the fast-paced nature of day trading can lead to increased stress levels.
- Market Volatility: Intraday price volatility can result in unpredictable market movements, leading to unexpected losses.
- Requires Discipline: Day trading requires discipline to adhere to trading plans and avoid emotional decision-making.
Consider the following illustration of a day trading setup on the EUR/USD currency pair:
In this example, the USD/JPY pair exhibits intraday price fluctuations, providing opportunities for day traders to profit from short-term movements. Mark analyzes intraday price charts and identifies a bullish breakout pattern on the USD/JPY pair. He enters a long position as the price breaks above a key resistance level, aiming to capitalize on the upward momentum during the trading session.
-
Scalping Strategy
Scalping is a high-frequency trading strategy where traders execute multiple trades to capitalize on small price fluctuations. It involves making numerous small trades to profit from short-term price movements within the same trading session.
Traders employing this strategy focus on exploiting minor price movements in highly liquid markets to generate quick profits. Scalping requires trading instruments with tight bid-ask spreads to minimize transaction costs.
Scalpers rely heavily on technical indicators and chart patterns to identify short-term trading opportunities. They must act swiftly and precisely to enter and exit trades at optimal price levels.
Consider the following illustration of a scalping setup on the GBP/USD currency pair:
In this example, the EUR/JPY pair exhibits rapid price fluctuations, providing opportunities for scalpers to profit from short-term movements. Sarah identifies a short-term price pattern on the EUR/JPY currency pair using technical analysis indicators. She executes multiple quick trades, entering and exiting positions within minutes to capture small price movements and generate profits.
Pros
- Quick Profits: Scalping offers the potential for rapid profit accumulation from multiple trades executed within a short period.
- Reduced Overnight Risk: Scalpers do not hold positions overnight, eliminating exposure to overnight market events.
- Minimal Market Exposure: Scalping strategies aim to minimize exposure to market volatility by holding positions for short durations.
Cons
- High Transaction Costs: The frequent execution of trades can lead to increased transaction costs, impacting overall profitability.
- Intense Focus: Scalping requires intense concentration and focus to monitor price movements and execute trades promptly.
- Stressful Environment: The fast-paced nature of scalping can be mentally demanding and stressful for traders.
-
Swing Trading
Swing trading involves capturing medium-term price movements by identifying market swings within a trending or range-bound market. The trading strategy aims to profit from price swings over a period of days to weeks. Traders employing this strategy focus on identifying market trends and entering positions at opportune times to capture potential price movements.
Successful swing trading requires patience to wait for optimal entry and exit points, along with disciplined risk management. Swing traders often use indicators such as moving averages, MACD, and RSI to confirm trend direction and potential entry/exit points.
Consider the following illustration of a swing trading setup on the USD/JPY currency pair:
In this example, the USD/JPY pair exhibits a clear uptrend, providing opportunities for swing traders to enter long positions during pullbacks. John identifies a bullish trend reversal pattern on the USD/JPY daily chart, signaling a potential swing trading opportunity. He enters a long position near the swing low and sets a profit target based on the projected price extension, aiming to capture the upward momentum over the following days.
Pros
- Profit Potential: Swing trading offers the potential for significant profits by capturing intermediate price movements within trending markets.
- Reduced Stress: Compared to day trading, swing trading involves fewer trades and allows for more relaxed decision-making.
- Flexibility: Swing trading can be adapted to various timeframes and market conditions, providing flexibility for traders.
Cons
- Overnight Risk: Swing traders hold positions overnight, exposing them to potential market gaps and overnight volatility.
- Delayed Gratification: Swing trading requires patience as trades may take days or weeks to reach their profit targets.
- Market Noise: Market noise and short-term fluctuations can sometimes trigger premature exits or false signals for swing traders.
-
Carry Trade Strategy
Carry trade strategy entails borrowing funds in a currency with low-interest rates and investing in a currency with higher interest rates. Traders employing this strategy aim to profit from the interest rate differential between two currencies, known as the “carry,” while potentially benefiting from exchange rate movements.
Carry traders carefully select currency pairs with stable economies and interest rate outlooks to minimize risk. Carry trades are often held for extended periods to accrue interest income, rather than short-term price movements. Effective risk management is crucial to mitigate potential losses from adverse exchange rate fluctuations.
Consider the following illustration of a carry trade setup involving the AUD/JPY currency pair:
In this example, the Australian Dollar (AUD) offers a higher interest rate compared to the Japanese Yen (JPY), making it an attractive candidate for carry trading. Emily borrows Japanese Yen (JPY) at a low-interest rate and converts it into Australian Dollars (AUD) to invest in Australian government bonds.
By holding the AUD-denominated assets, Emily earns interest income from the higher Australian interest rates, while potentially benefiting from AUD appreciation against JPY.
Pros
- Passive Income: Carry traders earn interest income from the interest rate differential between two currencies, providing a steady stream of passive income.
- Diversification: Carry trade strategy offers diversification benefits as it is less correlated with traditional asset classes such as stocks and bonds.
- Potential for Capital Appreciation: In addition to interest income, carry traders may profit from favorable exchange rate movements, enhancing overall returns.
Cons
- Exchange Rate Risk: Carry trades are exposed to exchange rate fluctuations, which can erode profits or lead to losses if currencies depreciate.
- Interest Rate Changes: Unexpected changes in interest rates by central banks can impact carry trade profitability and require adjustments to positions.
- Leverage Dependency: Carry trades often utilize leverage to amplify returns, increasing the risk of significant losses if markets move against the trader.
-
Breakout Strategy
Breakout strategy aims to enter trades when the price breaks out of a defined price range or chart pattern. It involves entering trades when the price breaches a predefined support or resistance level, signaling potential trend continuation.
Traders using this strategy seek to capitalize on significant price movements following the breakout of key technical levels or chart patterns. They identify key support and resistance levels or chart patterns, such as triangles or rectangles, to anticipate potential breakouts.
Breakout traders wait for confirmation of the breakout, such as increased volume or a close above/below the breakout level, before entering trades. Breakout strategies are more effective in volatile market conditions, as increased volatility often leads to stronger price movements. Effective risk management is essential to mitigate losses in case of false breakouts or adverse market movements.
Consider the following illustration of a breakout trading setup on the EUR/USD currency pair:
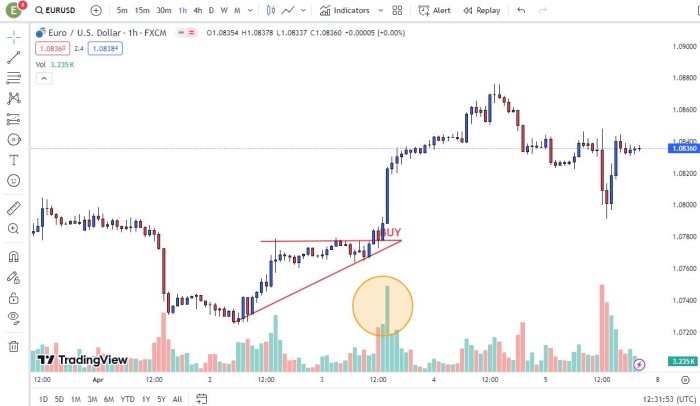
In this example, the EUR/USD price breaks out above a key resistance level, signaling a potential uptrend continuation. Sarah identifies a symmetrical triangle pattern forming on the EUR/USD chart, anticipating a breakout to the upside. She waits for confirmation of the breakout with increased volume and a close above the triangle’s upper trendline before entering a long position.
Pros
- Profit Potential: Breakout strategies offer the potential for significant profits by capturing large price movements following breakout events.
- Clear Entry and Exit Signals: Breakouts provide clear entry and exit signals, making it easier for traders to plan their trades and set profit targets.
- Trend Confirmation: Successful breakouts often confirm the continuation of existing trends, allowing traders to ride the momentum for extended periods.
Cons
- False Breakouts: Market noise and false breakouts can lead to losses if traders enter positions prematurely before confirmation signals.
- Whipsaw Movements: Breakout strategies are susceptible to whipsaw movements, where the price breaks out briefly before reversing direction, causing losses for traders.
- Risk of Missed Trades: Breakout traders may miss trades if they are overly cautious and wait for excessive confirmation signals, leading to missed opportunities.
-
News Trading
News trading involves capitalizing on market movements triggered by significant economic or geopolitical events. Traders employing news trading monitor economic calendars and news feeds to identify upcoming events with the potential to impact currency, commodity, or equity markets.
Traders focus on high-impact economic indicators, central bank announcements, geopolitical developments, and other news events with the potential to influence market sentiment. News traders analyze forecasts, consensus estimates, and historical data to anticipate the market’s reaction to the upcoming news release.
Traders enter positions either moments before the news release (pre-positioning) or immediately after, depending on their strategy and risk tolerance. Effective risk management is crucial due to the heightened volatility and rapid price movements associated with news trading.
Consider the following illustration of a news trading setup during a central bank interest rate decision:
Traders anticipate the market’s reaction to the central bank’s interest rate decision and enter positions accordingly. John monitors the economic calendar and identifies an upcoming non-farm payrolls (NFP) report, a high-impact news event for the USD.
Anticipating a bullish outcome, John pre-positions by entering a long USD position moments before the NFP release. John’s analysis pays off as the NFP report surpasses expectations, leading to a sharp appreciation of the USD against major currencies.
Pros
- High Volatility: News events often trigger sharp and rapid price movements, offering significant profit opportunities for well-prepared traders.
- Short-Term Gains: News trading can yield quick profits within a short time frame, making it attractive for traders seeking short-term opportunities.
- Clear Catalysts: News releases serve as clear catalysts for market movements, providing identifiable entry and exit points for traders.
Cons
- Increased Risk: News trading carries heightened risk due to the unpredictability of market reactions and the potential for rapid price swings.
- Slippage and Spread Widening: During high-impact news releases, traders may experience slippage and widened spreads, impacting trade execution and profitability.
- Emotional Pressure: Managing emotions such as fear and greed is challenging during volatile news events, leading to impulsive decision-making and potential losses.
-
Retracement Trading
Retracement trading involves profiting from temporary price reversals within an established trend in financial markets. Traders capitalize on temporary pullbacks within a prevailing market trend.
Traders employing retracement trading identify instances where prices temporarily reverse against the primary trend before resuming their original direction. They first identify a well-established trend in the market, either bullish or bearish. They then look for temporary price retracements or pullbacks against the prevailing trend.
Traders enter positions when the price retracement reaches a predetermined level of support or resistance, indicating a potential reversal. Effective risk management strategies, such as setting stop-loss orders, are essential to mitigate losses if the retracement continues against the trend.
Consider the following illustration of a retracement trading setup in an uptrend:
Traders identify the prevailing uptrend and wait for a pullback to a key support level (e.g., a Fibonacci retracement level or a previous resistance-turned-support level).
Sarah identifies an uptrend in the EUR/USD currency pair and waits for a retracement to the 50% Fibonacci retracement level. Once the price retraces to the 50% Fibonacci level and shows signs of bullish reversal, Sarah enters a long position.
Pros
- Riding the Trend: Retracement trading allows traders to capitalize on short-term price reversals while riding the overall trend.
- Enhanced Risk-Reward Ratio: By entering trades at favorable retracement levels, traders can achieve attractive risk-reward ratios.
- Clear Entry Signals: Retracement levels, often based on Fibonacci retracement levels or support/resistance zones, provide clear entry signals for traders.
Cons
- False Signals: Not all retracements result in trend reversals, leading to potential losses if the retracement turns out to be a temporary pullback rather than a reversal.
- Timing Challenges: Identifying the precise end of a retracement and the resumption of the primary trend can be challenging, leading to missed opportunities or premature exits.
- Emotional Discipline: Retracement trading requires discipline to adhere to predefined entry and exit criteria, as emotional reactions to market fluctuations can lead to impulsive decisions.
-
Grid Trading
Grid trading is a strategy where traders capitalize on price fluctuations within a predefined range or grid structure. Traders place buy and sell orders at predetermined intervals above and below a set price level. Traders establish a grid structure by placing buy and sell orders at regular intervals above and below the current price.
Traders using grid trading aim to profit from market volatility by exploiting price movements within a specified range. Grid trading is most effective in markets exhibiting range-bound behavior, where prices fluctuate within a defined range over time.
Grid trading strategies can be automated using trading algorithms to execute orders according to predefined parameters. Traders must carefully manage position sizes to ensure that the grid structure remains balanced and aligned with risk management principles.
Consider the following illustration of a grid trading setup in a range-bound market:
Traders establish a grid structure by placing buy orders (green) and sell orders (red) at predetermined intervals above and below the current price.
John implements a grid trading strategy in AUD/USD pair that has been trading within a narrow range. He sets up a grid with buy orders at every 20-pip interval above the current price and sell orders at every 20-pip interval below the price.
Pros
- Profit Potential: Grid trading can generate profits from price fluctuations within the predefined range without requiring the market to establish a clear trend.
- Automation: Automated grid trading systems can execute orders automatically, eliminating the need for manual intervention and allowing for continuous monitoring of market conditions.
- Diversification: Grid trading allows traders to diversify their trading strategies by simultaneously trading multiple currency pairs or assets within different grid structures.
Cons
- Market Volatility: High levels of market volatility can lead to rapid price movements that disrupt the grid structure and result in unexpected losses.
- Limited Profit Potential: Grid trading strategies may generate consistent but relatively small profits compared to strategies that capitalize on trending markets.
- Risk Management: Maintaining proper risk management is crucial in grid trading to prevent excessive losses, particularly during periods of heightened volatility.
How to Choose the Best Forex Trading Strategy?
Finding the right forex trading strategy involves experimentation, self-awareness, and ongoing adaptation. Here’s how you can determine which strategy suits you:
- Understand Your Goals: Determine your trading objectives—whether you’re aiming for short-term gains, long-term growth, or a mix of both. This will help you narrow down suitable strategies.
- Assess Your Risk Tolerance: Know how much risk you’re comfortable with. Some strategies are more conservative, aiming for steady gains, while others are higher risk with potential for larger returns.
- Research Different Strategies: Explore various forex trading strategies such as trend following, breakout trading, range trading, scalping, etc. Understand how they work and their typical performance under different market conditions.
- Consider Market Conditions: Some strategies work better in specific market conditions (e.g., trending markets vs. ranging markets). Choose a strategy that aligns with the current market environment.
- Backtest Strategies: Use historical data to test different strategies and see how they would have performed. This helps gauge their effectiveness and potential profitability.
- Evaluate Time Commitment: Decide how much time you can dedicate to trading. Some strategies require frequent monitoring (like day trading), while others are more hands-off (like swing trading).
- Factor in Costs: Consider transaction costs, spreads, and other fees associated with the strategy. High-frequency strategies may incur more costs due to increased trading frequency.
- Demo Trade: Before committing real capital, practice the strategy on a demo account. This allows you to see how the strategy performs in real-time without risking money.
- Monitor and Adapt: Even the best strategies may need adjustments over time. Continuously monitor performance and adapt as needed based on changing market conditions or personal preferences.
- Seek Advice and Education: Consider seeking advice from experienced traders or taking forex trading courses to deepen your understanding of different strategies and improve your skills.
FAQs
Can beginners use advanced trading strategies?
While beginners can explore various strategies, starting with simpler approaches is advisable to build foundational knowledge and skills.
How do I know if a strategy is suitable for my risk tolerance?
Consider the strategy’s historical performance, drawdowns, and risk-reward ratio to assess its alignment with your risk appetite.
Is it necessary to stick to one strategy or can I use multiple simultaneously?
It’s possible to use multiple strategies based on market conditions, but ensure you fully understand each strategy and its implications.